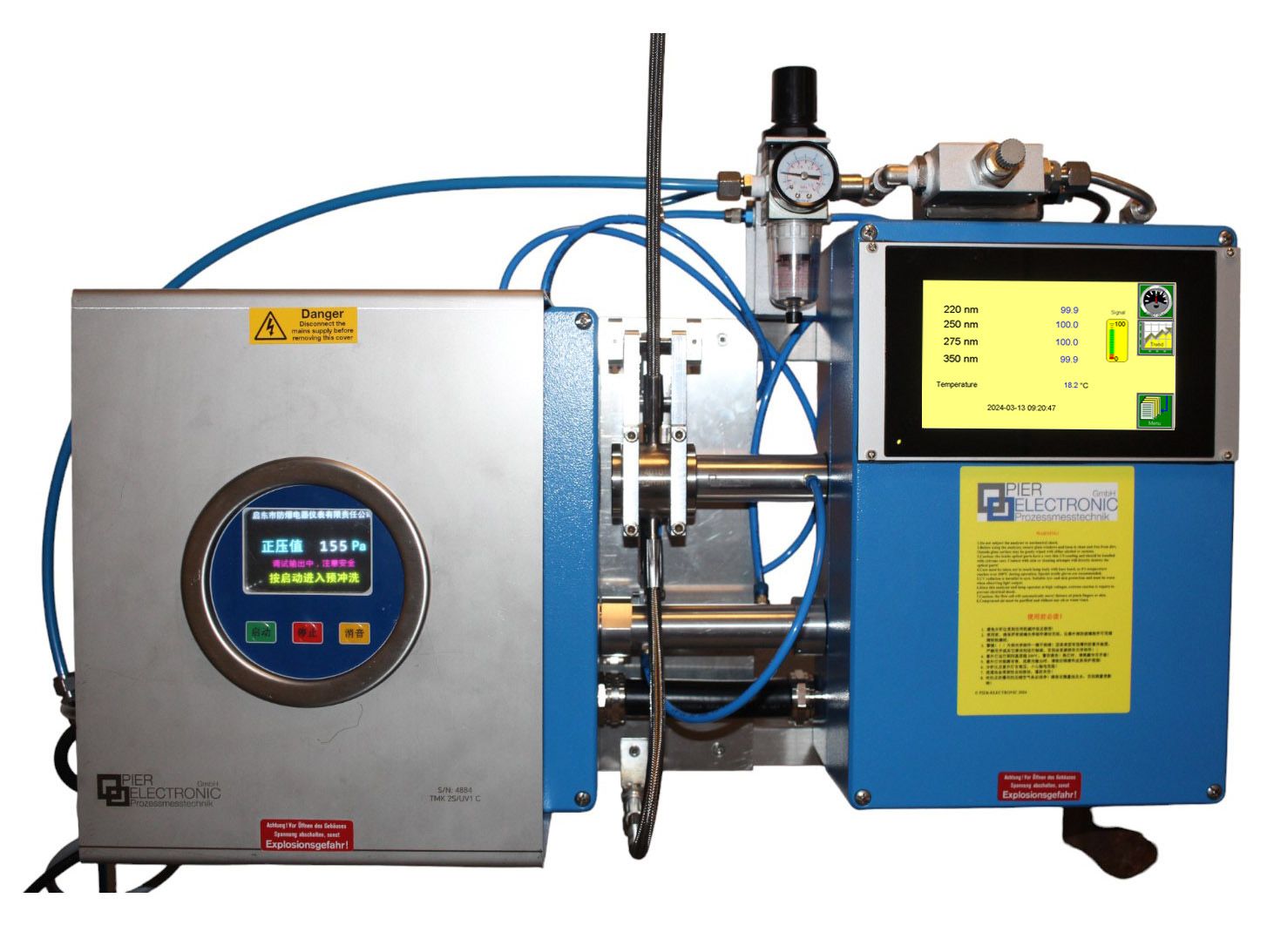
Willkommen bei
PIER-ELECTRONIC GmbH
Prozessmesstechnik
Fertigungskontrolle im laufenden Produktionsprozess
Qualitätskontrolle:
Berührungslose Online-Messung am Produkt
Prozessoptimierung:
Echtzeit-Daten vom Produkt zur Steuerung
Komfort:
Intuitive Bedienung
Zuverlässigkeit:
Einfache Kalibrierung
Service:
Langfristige Wartung direkt vom Hersteller
Feuchtemessung
und Verunreinigungen
Mit unserem optischen Messverfahren können Sie den Wassergehalt oder viele andere Komponenten in Ihrem Produkt überwachen – sei es Feststoff oder Flüssigkeit, Schüttgut oder Gas!
- Messung der Restfeuchte beim Trocknen
- Kontrolle des Wassergehalts von Bremsflüssigkeit
- Überwachung von toxischen Substanzen im Abwasser
- Detektion von überschüssigen Reagenzien
- und vieles mehr…
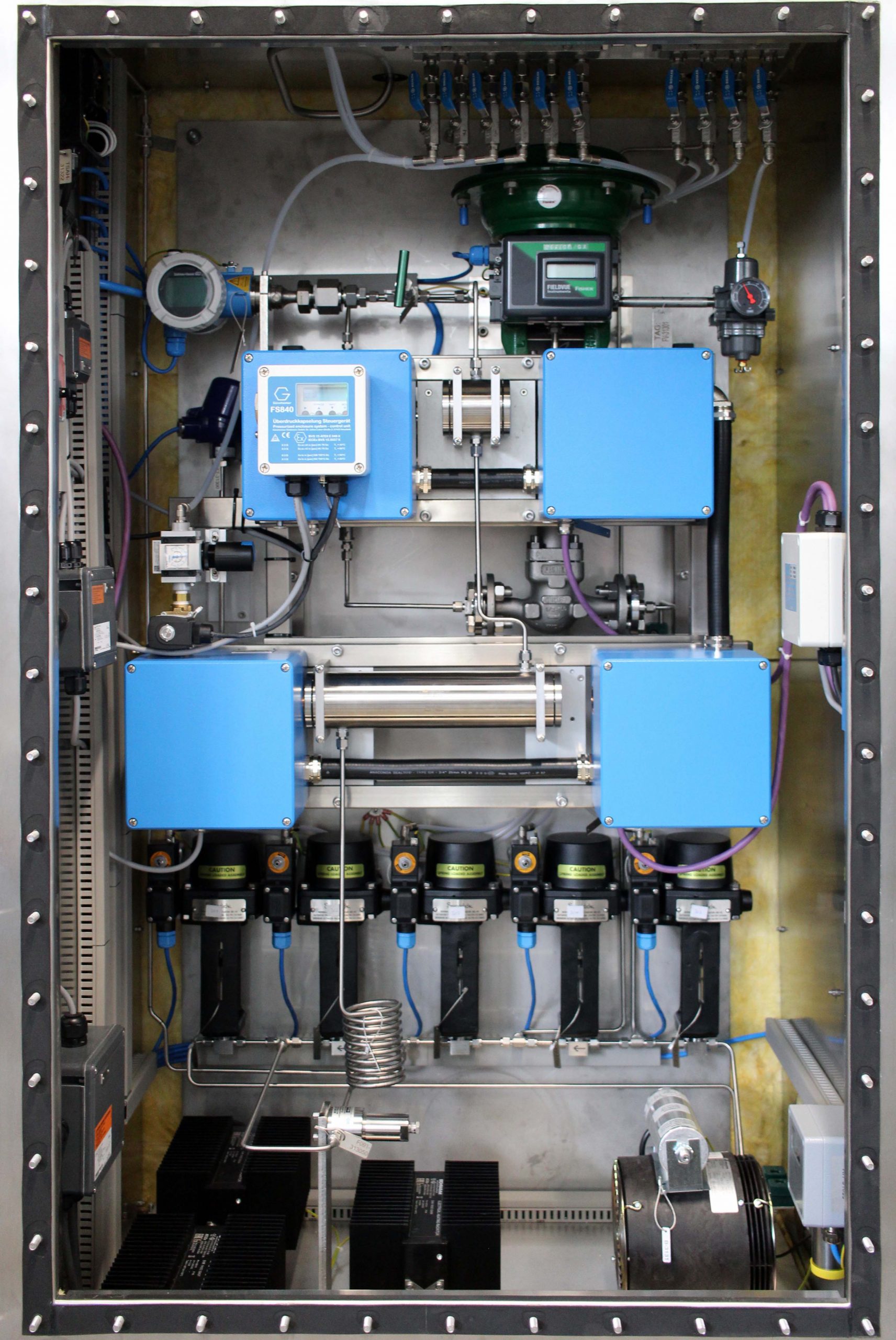
Hohe Qualität für Ihre Qualitätssicherung
Wir sind ein kleiner, freundlicher mittelständischer Betrieb im Main-Taunus-Kreis. Seit 50 Jahren entwickeln und liefern wir Mess-Systeme, die intuitiv zu bedienen sind und im laufenden Produktionsprozess die Qualität verschiedener Produkte sicherzustellen helfen.
Und was können wir für Sie tun?
Unsere Dienstleistungen umfassen Beratung, Tests, physikalische Umsetzung, technische Fertigung, Installation vor Ort, Schulung, Kalibrierung, Wartung sowie Reparaturen. Senden Sie uns noch heute eine Anfrage, damit wir Ihre Anwendung besprechen können. Wir stehen Ihnen gerne mit Rat und Tat zur Seite, um die optimale Lösung für Ihre Mess-Konfiguration zu erarbeiten.